1. Introduction SLaMA-Approach
The Simple Lateral Mechanism Analysis - SLaMA - is a simple nonlinear analysis technique suitable for unreinforced masonry low-rise buildings with either rigid or flexible floors types. The SLaMA-approach is based on a mechanism-based failure modes for masonry, as described in NPR 9998:2018 (NPR) Annex G.6.2 for the in-plane (IP) assessment, and integrated with the NLKA and probabilistic methods, as explained in Annex H and J of the NPR, for the out-of-plane (OOP) evaluation. Floors and roofs are addressed following the New Zeeland seismic code of 2017 for the assessment of existing structures, section C8. Connections are checked according to the diaphragm actions found in the floor/roof and OOP. Foundations are checked according to the NPR chapter 10. The SLaMA-method is based on mean properties of materials and structural elements.
More background information about SLaMA and NLPO in general can be found in Paragraph 1.1 Introduction and 1.2 Non-Linear analysis methods and knowledge development of the NLPO/NLTH protocol on Gitlab and in Annex G.10 of the NPR.
1.1. References
The references with the additional information used in SLaMA-Approach are given in table below.
Table 1 - References |
|
|---|---|
Reference number |
Link |
[1] |
NLPO/NLTH Protocol Paragraph 1.1 Introduction and 1.2 Non-Linear analysis
methods and knowledge development (see Introduction)
|
[2] |
NLPO/NLTH Protocol Chapter 2 (see Phase 1 - Starting phase) |
[3] |
Linking to former NLPO/NLTH BSC reporting phase instructions |
[4] |
|
[5] |
L4-excelsheet MOVED TO SHAREPOINT |
[6] |
|
1.2. General SLaMA assessment workflow
The workflow consists of multiple phases. These phases are summarized in a flowchart and more in detail in the following chapters. For each phase, products are delivered (deliverables) that will be part of the final report.
Note
Store all your work in the appropriate Box-folders at all times. Preferably use Box Drive or the Box Sync.
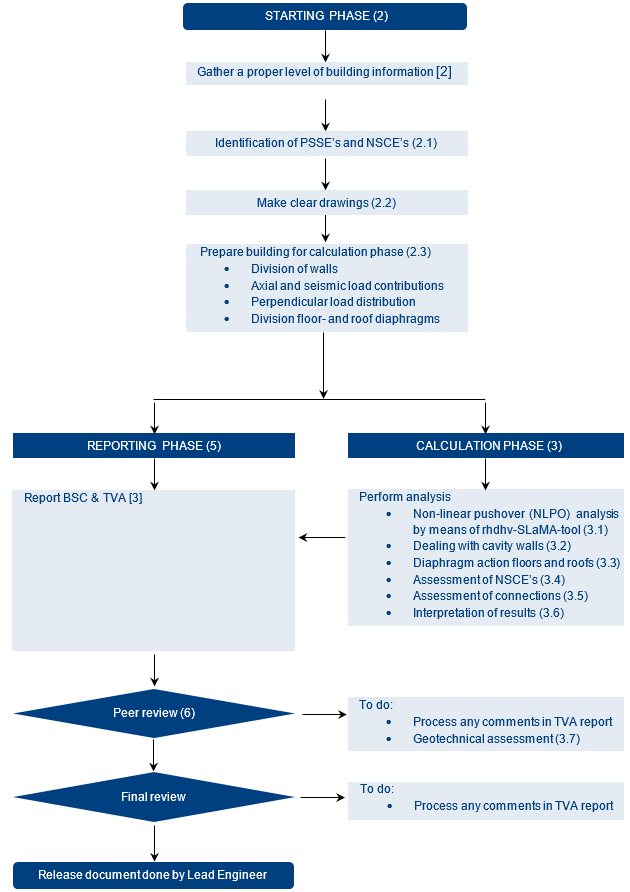
Figure 1.7 Flowchart SLaMA assessment
1.3. Definitions and acronyms
Table 2 - Definitions and acronyms |
|
|---|---|
Definition |
Description |
ADRS |
Acceleration-displacement response spectrum (spectra) |
Diaphragm |
A horizontal structural element (floors and roof structures) that are connected to the
vertical lateral force-resisting elements around it and that distributes earthquake lateral
forces to elements, such as masonry walls, of the primary lateral system
|
NCE |
Niet-Constructieve Elementen (Non Structural Elements) |
NLKA |
Non-linear kinematic analysis |
NLPO |
Non-Linear Push-Over |
NSCE |
Non-seismische constructieve elementen (Non-Seismic Structural Elements) |
NPR |
Nederlandse Praktijk Richtlijn (Dutch guideline for earthquake resistant design) |
PRBE |
Potential Risk Building Elements |
PSSE |
Primary and secondary seismic elements |
SLaMA |
Simple Lateral Mechanism Analysis (Type of NLPO) |
Subsystem |
Contains the lateral resisting elements, such as structural walls, that contributes to the
in-plane seismic resistance in that axis. Also contains other structural elements of the
structure that may not contribute to the resistance of subsystem but contributes as
seismic mass according to a tributary area distribution
|
URM |
Unreinforced masonry; A member or element comprising masonry units connected
together with mortar and not containing any steel, timber, cane or other reinforcement
|
1.4. Element types
Elements can consist of primary, secondary, non-seismic structural and non-structural elements.
A primary seismic element is part of the system to withstand the horizontal effect of earthquake action. A secondary seismic element is an element that does not contribute to resisting the horizontal earthquake action but transfers the vertical loads from its own weight and connected elements (such as supported floors, roofs) to the foundations during the earthquake. The collection of the primary and secondary seismic elements is abbreviated to PSSE’s (Primary and Secondary Seismic Elements).
Non-seismic structural elements (NSCE, Dutch: Niet-Seismische Constructieve Elementen) are elements that are not part of the earthquake resistance system, but which are denoted as structural elements according to the Dutch Building Decree (Bouwbesluit, art. 1.5.1.7). Examples of NSCE are non-load-bearing interior walls, chimneys, parapets, stairs, balconies and gallery slabs. During an earthquake, an NSCE only has to transfer the earthquake load due to its own weight combined with the relevant quasi-permanent load to the foundation, whereby collapse of the structural element does not lead to progressive collapse. NSCE must be classified into four types (type 1 - 4). The vertical elements such as walls, roof curbs, chimneys, etc. are tested using the NLKA method, in accordance with Annex H of the NPR 9998:2018.
Non-structural elements (NCE) are elements that are not a structural element according to the building decree. Examples are suspended ceilings, pipes and cabinets. Non-structural elements do not need to be assessed. The NPR 9998:2018 does provide recommendations for the assessment of non-structural elements.
Table 3 - Local failure of construction part |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
PSSE |
NSCE |
NCE |
||
Primary
seismic
elements
|
Secondary
seismic
elements
|
Non-seismic
structural
elements
|
Non-structural
elements
|
|
Bearing walls |
x |
x |
||
Steel structure |
x |
|||
Steel structure
braced bays and moment
resisting frames
|
x |
|||
Concrete structure |
x |
x |
||
Timber structure |
x |
x |
||
Floors including
ground floor
and roofs
|
x |
|||
Non-load bearing
masonry walls - near
escape routes
|
x |
|||
Non-load bearing
masonry walls - other
|
x |
|||
Balcony |
x |
|||
Gallery |
x |
|||
Gallery - escape route |
x |
|||
Outer cavity leaf
near escape route
|
x |
|||
Outer cavity leaf
at height ≤3,0m
|
x |
|||
Platforms |
x |
|||
Architectural steel |
x |
|||
Lightweight non-load
bearing partition
walls
|
x |
|||
Lightweight non-load
bearing partition
walls - near escape
route
|
x |
|||
Stairwell / stairs |
x |
|||
Emergency stairwell |
x |
|||
Facade elements
(ornaments)
|
x |
|||
Canopies |
x |
|||
Canopies
near escape route
|
x |
|||
Atrium |
x |
|||
Chimney
(if no PRBE )
|
x |
|||
Roof curbs, statues
(if no PRBE )
|
x |
|||
Roof curbs, statues
near escape route
(if no HRBE )
|
x |
|||
Ceiling |
x |
|||
Heating, pipes etc. |
x |
|||
Elevators |
x |
|||
Cabinets (furniture) |
x |
|||
x - probable category in which the building part falls, this must be assessed object-specific for each part.