How to use the VIIA servers
Introduction
This how-to guide explains how to use the VIIA servers to perform DIANA analysis in a most optimised way. It demonstrates which items should be checked before, during and after the calculation. This guide does not provide insight in solving convergence problems or general dcf-settings.
Servers
For the VIIA project we have 9 servers available to perform our calculations.
Server name |
Usage |
|---|---|
NLAMELAPAPS005 |
DIANA |
NLAMELAPAPS006 |
DIANA |
NLAMELAPAPS007 |
DIANA |
NLAMELAPAPS008 |
DIANA |
NLAMELAPAPS009 |
DIANA |
NLAMELAPAPS010 |
ABAQUS |
NLAMELAPAPS011 |
DIANA |
NLAMELAPAPS012 |
DIANA |
NLAMELAPAPS013 |
DIANA / ABAQUS |
The servers have been purchased by VIIA to assist engineering with the long running calculations. The servers are located on the RHDHV network and maintained by RHDHV WPS.
Why running analyses on servers?
The seismic analyses for VIIA are performed on big complex advanced FEM-models. The complete model is divided in small elements (+100k) and require many iterations depending on the calculation method (MRS/NLPO/NLTH). The non-linearity of the materials and connections increase the number of iterations required to find the accepted solution. Not only the size a complexity of the model, but also the requested collection of output items (and writing to disk) influences the speed of the analysis.
In our VIIA experience we have seen analysis that are running for ~5 weeks max. Running these kinds of calculations is not possible on laptops and provides a chance to improve the efficiency of the calculation. Next to that the servers are equipped with big SSD-drives to optimise the writing process.
Login
To gain access to the servers, you need a SZ1 account. This can be request by sending a email to reinier.ringers@haskoning.com. When you have the SZ1 credentials you can can email your SZ1-username and VIIA-team to reinier.ringers@haskoning.com or jurriaan.floor@haskoning.com, with the request to give you access to the VIIA-servers. Once you have granted access you need to use the ‘remote desktop connection’ feature to login on the server. Login is not required for the exchange drive, you even do not have to have access rights to the server at all. It is required that you are connected to the RHDHV network (AlwaysOn-UserTunnel). If you experience problems contacting the network please inform the ICT servicedesk.
Figure 71 Make sure you are connected to the RHDHV network.
Please be sure to you are using the proper setup of the remote desktop connection. It should look like the figure below, with the application of the proper server number and personal number.
Figure 72 Login menu.
Only two users can be logged in at the same time, although multiple users can be disconnected (and running calculations). When two users have logged in, you will get a notification. You can request those users for access, they need to disconnect then.
MYVIIA use on the servers
To be able to connect to MYVIIA on the servers your MYVIIA credentials should be stored on the server. This has to be done once per server. To store the MYVIIA credentials a batch file can be used. This batch file is stored on the server at this location ‘E:VIIAset_MYVIIA_credentials_on_server.bat’. If the file is not present you can download it here:
Exchange
Every server has an exchange folder that is used to transfer the files. These folders are accessible from the server and also on your local workstation. The exchange folders of the different servers are:
Policies
Because we have multiple people using the servers for their objects in VIIA. This requires some policies for cooperation.
Sign out
Sign out when you leave the server and do not have any analysis running and when you are not planning to reconnect the
same day. Be careful when you sign out not to select Shut Down or Restart.
Disconnect
You can disconnect if you have a calculation running or are planning to reconnect the same day. Be aware that any
opened program uses RAM-memory. Disconnecting with an open DIANA GUI with model is slowing the calculations on the
server.
Using DIANA GUI
You can use the DIANA GUI on the server, keep in mind that the hardware is not optimised for rendering. And because of
the RAM usage try to minimize this. Always close the GUI when finished to free up the memory. Pycharm is installed on
the servers, so you can use viiaPackage on the server. Keep in mind to use the correct version.
Installing other software
Installing other software on the servers is not allowed. Please send a request to one of the server admins.
Performing calculations
Only run calculations on server from command-box. Inquire with the other users if you can run calculation. When the
calculation is finished remove the filos-file. You are responsible for keeping an eye on the disk-usage. When the disk
is full the analysis will stop, also those of your colleagues. The total amount of used disk should not exceed 150Gb,
or even less, depending on the number of users on the server. You can temporary exceed the 150Gb when you discuss this
with the other users.
Compress files for transferring data
It might be that you experience bad connections. It is advised to compress and/or split large files (with winrar),
then you are less dependent on the stability of your connection to the server. Some additional remarks:
Many small files can be better merged into one (several small files demand more from network then one big file).
Settings for compressing: More compressing is more efficient then fast compression.
Outside business hours the company network is more stable.
Don’t store data of older analyses on server!
Use a batch file to run a calculation
Always start an analysis from batch file. Such a file will automatically remove the filos-file (del *.ff) and provide
more space for colleagues to perform analyses. See Batchfile.
Keep track of your analysis
Check how many calculations are running before you start (see Server capacity check). Discuss with your
colleagues on the server if you can switch on a calculation. During the analysis check if it is performing as expected
(and correctly selected result items are obtained). Check if your disk usage is okay. When disk is full your
calculation will be aborted, but also those of you colleagues.
Only run 1 or 2 signals
When you are in the process of modelling and strengthening your model, select 1 or 2 signals to be used to test your
model. It is not useful to run all signals as they probably will not be successful. Only when you completely ran 1 or 2
signals and completely checked if they comply, then you can switch on all other signals.
viiaPackage
Use the viiaPackage to handle the results, but do not use it to generate complete reports. Check the version of the
viiaPackage.
DIANA software
The DIANA versions provided on the server are the versions that are mentioned in the UPR.
Clean your recycle bin
When you remove or delete files they end up in your recycle bin. There they still occupy space on the disks. Incidents
in the past resulted that the total amount of trash in the recycle bin caused a full disk failure.
Server capabilities
This section contains the current capabilities of the VIIA servers.
NLAMELAPAPS005 |
NLAMELAPAPS006 |
NLAMELAPAPS007 |
NLAMELAPAPS008 |
NLAMELAPAPS009 |
NLAMELAPAPS010 |
NLAMELAPAPS011 |
NLAMELAPAPS012 |
NLAMELAPAPS013 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Domain |
corporateroot.net |
corporateroot.net |
corporateroot.net |
corporateroot.net |
corporateroot.net |
corporateroot.net |
corporateroot.net |
corporateroot.net |
corporateroot.net |
Operating system |
Windows Server 2019 |
Windows Server 2019 |
Windows Server 2019 |
Windows Server 2019 |
Windows Server 2019 |
Windows Server 2019 |
Windows Server 2019 |
Windows Server 2019 |
Windows Server 2019 |
System type |
64-bit, x64-based processor |
64-bit, x64-based processor |
64-bit, x64-based processor |
64-bit, x64-based processor |
64-bit, x64-based processor |
64-bit, x64-based processor |
64-bit, x64-based processor |
64-bit, x64-based processor |
64-bit, x64-based processor |
RAM |
512Gb |
512Gb |
576Gb |
576Gb |
576Gb |
576Gb |
576Gb |
576Gb |
512Gb |
Processor |
Intel® Xeon® CPU E5 E5-2687W v3 @ 3.10GHz (2 processors) |
Intel® Xeon® CPU E5 E5-2687W v3 @ 3.10GHz (2 processors) |
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6256 CPI @ 3.60GHz 5.59 GHz (2 processors) |
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6256 CPI @ 3.60GHz 5.59 GHz (2 processors) |
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6256 CPI @ 3.60GHz 5.59 GHz (2 processors) |
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6256 CPI @ 3.60GHz 5.59 GHz (2 processors) |
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6256 CPI @ 3.60GHz 5.59 GHz (2 processors) |
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6256 CPI @ 3.60GHz 5.59 GHz (2 processors) |
Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8358 CPU @ 2.60GHz (2 processors) |
Sockets |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
Cores |
20 |
20 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
24 |
Logical processors (threads) |
40 |
40 |
48 |
48 |
48 |
48 |
48 |
48 |
48 |
Diskdrive 1 |
SSD C: 80Gb D: 106Gb |
SSD C: 80Gb D: 106Gb |
SSD C: 80Gb D:366Gb |
SSD C: 80Gb D:366Gb |
SSD C: 80Gb D:366Gb |
SSD C: 80Gb D:365Gb |
SSD C: 81Gb D:365Gb |
SSD C: 81Gb D:365Gb |
SSD C: 81Gb D:812Gb |
Diskdrive 2 |
SSD E: 1341Gb |
SSD E: 1341Gb |
SSD E: 1341Gb |
SSD E: 1341Gb |
SSD E: 1341Gb |
SSD E: 1341Gb |
SSD E: 1341Gb |
SSD E: 1341Gb |
SSD E: 2180Gb |
Diskdrive 3 |
SSD F: 1341Gb |
SSD F: 1341Gb |
SSD F: 1341Gb |
SSD F: 1341Gb |
SSD F: 1341Gb |
SSD F: 1341Gb |
SSD F: 1341Gb |
SSD F: 1341Gb |
USSD R: 199Gb |
Diskdrive 4 |
SSD G: 3490Gb |
||||||||
DIANA 10.7 |
2023-06-15 |
2023-10-05 |
2023-10-05 |
2023-06-15 |
|||||
DIANA 10.9 |
2024-06-20 |
2024-06-20 |
2024-06-20 |
2024-06-20 |
2024-06-20 |
2024-06-20 |
2024-06-20 |
2024-06-20 |
2024-06-20 |
DIANA 10.10 |
2025-08-18 |
||||||||
COMSOL |
|||||||||
ABAQUS |
2020 |
2022 |
|||||||
PyCharm |
2025.2 |
2018.2 |
2024.1 |
2024.1 |
2020.2 |
2024.2 |
2023.2 |
2025.2 |
2025.2 |
Calculation process basics
The calculation process consists of several parts. It should be noted that after meshing the problem becomes basically a pure math-problem. In the Diana manual the calculation process is described, for instance in link and link.
To have some knowledge how to speed up the calculation some basic considerations are provided:
The amount of integration points with non-linear behaviour. (This should increase during the analysis so the calculation decreases) Note that during the iteration process integration points can become non-linear for a moment and can become linear again. Therefor modelling unnecessary parts non-linear will slow down the calculation.
Bad convergence behaviour; if the convergence criteria are not met the maximum number of iterations will be performed.
Times of setting up a new stiffness matrix. To be able to solve the matrix equation the stiffness matrix is inverted, this is a calculation costly operation. Note that there a different iteration-methods (such as Newton-Raphson and Secant) which uses different amount of times to set-up the stiffness matrix.
Ratio of steps and iterations. An iteration takes less time as setting up a new step. Nevertheless, to many iterations per step will not be time effective.
How to start a calculation
Before starting a calculation it’s important to check several items. This is not only necessary to be able to run your calculation but also to make it as fast as possible. When these basic checks are done one can start the actual calculation with a batch-file.
Input check
The DIANA-solver needs two files. The dat-file (data) which contains the model and the dcf-file (DIANA command file) with the properties for the actual analysis.
Number of threads
For an optimal calculation one should check if MAXTHR and NUMTHR is present in the dcf-file. These values represent how
many threads will be used for solving the stiffness matrix and the non-linear stresses. The values of both options
should be the same. If one is not specified or there is a difference the calculation can slow down. If the specified
number of threads is not available/free the solver will wait and consequently the analysis slows down. Note that
assigning more threads does not speed up the analysis in all cases. Using four threads has been estimated to be the most
efficient setting for the type of objects in the VIIA project.
Add the following command above the initialization phase (* FILOS) of the dcf-file:
>>> NUMTHR 4
Add the following command to the solver settings of each phase of the dcf-file:
>>> MAXTHR 4
For further explanation about the dcf-file, see How to DCF settings.
Output specification
For calculations with many steps one should take create care of the output which is specified. Writing output can take
a considerable amount of time especially for large models with many steps. Moreover, the needed disk-space increases
and the disk-space is limited. There are some basic principles one should consider:
Write only output that will be used in the assessment.
Write output at the right steps (ALL, LAST, or a specific interval for instance).
Prevent writing the same output multiple times.
Server capacity check
The capacity of the server is limited and should not be exceed. Three type of capacities should be checked before starting an analysis; CPU, memory (RAM) and disk.
Memory
For an optimal calculation process a lot of data is stored in the memory. If the data does not fit in the memory the
calculation slows down drastically or even stops. Before starting an analysis one should check if the calculation will
‘fit’ in the memory. In performance tab of the task manager one can find the available and used memory. One should add
the total size of all filos files to the used memory (search for *.ff at search bar in the right top corner in the
drive folder).
The following example demonstrates how to calculate the memory usage.
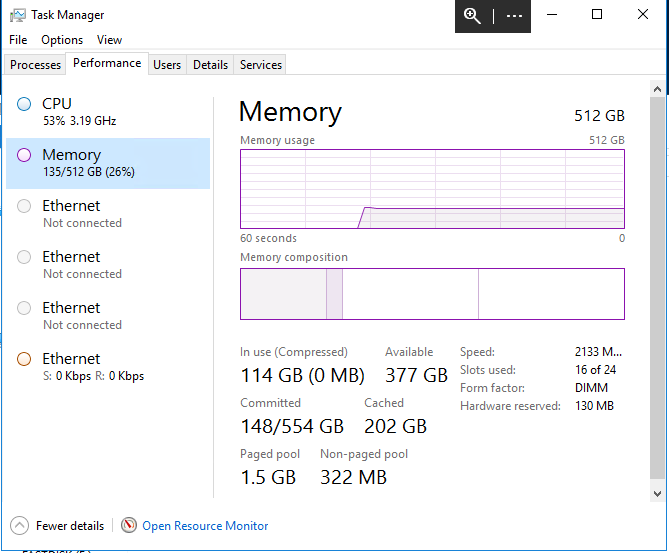
Figure 73 Task manager, performance on Memory tab.
The performance tab in the task manager shows the current memory usage. In this case 114GB. Now in the explorer search for all *.ff files in the E and F drives. Collect this total and add this to the one mentioned above: 114 + 98 = 212 Gb, which results in a memory usage of 41, which is fine.
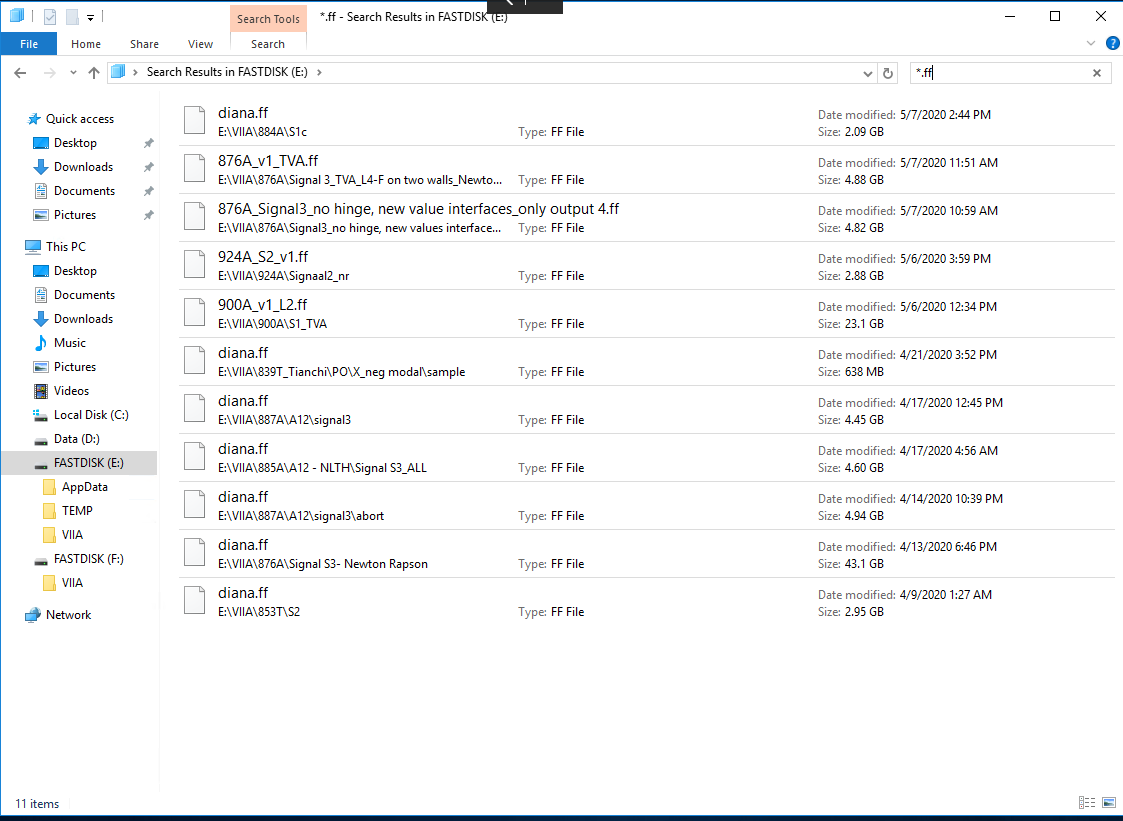
Figure 74 Search result for filos-files.
CPU
Keep in mind that implicit analyses will never use 100% CPU usage, with explicit you could reach that. The implicit
analysis can run perfect although CPU usage is not above 50%.
An analysis uses the specified amount of threads. One can check the occupation rate of the threads in the performance tab of the task manager. The best overview is given by the ‘logical processors’ view. You can change the view by right click on the graph and then Change graph to/logical processors. If all the threads are busy one shouldn’t start a new analysis.
Storage
The amount of available space of the drive on which the analysis is preformed should be checked. One should check how
many other calculation are running (search for *.ff at search bar in the right top corner in the drive folder) and
estimated how much space these will need. (see figure above)
Batchfile
A batch file is a script which originates from the DOS-era (pre-windows). It’s a basic but powerful way to automize tasks on a windows operating system. Batch files are simple text-files with a .bat-extension. You can read them with most text editors. On most systems they will automatically be executed by double clicking, be aware of that. As said, they can be powerful, also in executing wrong code!
Batch files can be used to start a DIANA calculation and afterwards delete the FilosFile. For starting a DIANA calculation with a batch file, the file should be called by the Diana-command box. By default, the DIANA-command box is set to start in your user folder at the C-drive. Calculations are executed on the E-drive. You can use a batch-file also to change folders. This requires precise mindset, because if you don’t update the folders, you have the risk of running the same analysis twice and losing the output files of the completed analysis.
You can make a batch file first as .txt file and later change the extension from .txt to .bat.
By default, viiapackage already generates batch files for the user when running a time history analysis, i.e., A4, A12 or A15. One batch file each named ‘VIIA-SIGNAL-BATCH.bat’ is generated inside the folder of every signal. This batch file runs the analysis of that signal. In addition, another batch file is generated inside the folder that contains the signal folders. This batch file is named ‘VIIA-MAIN-BATCH.bat’ and can be used to run the analysis of all the signals in that folder in parallel.
Batch command |
Usage |
|---|---|
echo |
‘echo’ is the print statement of a batch file, text after the echo command is printed in the command box. |
cd |
Change direction. This command is used to change folders. |
cd folder_name |
Going into a folder (it’s possible to combine folders: cd folder_1/folder_2). |
cd .. |
Going a level up in the folder structure. (it’s possible to go several folders up in one go cd ../..) |
cd /d E: |
Change to a drive. In this excample we want to go to the E-drive. |
rem |
Remark. You can use this before a line to comment this line. In python ‘#’ works the same. |
del file_name |
Delete the file. |
pause |
Pauses the batch file. Batch files automatically quite and closes the command box. Some commands are not written in the .out file of DIANA. Therefor it is useful to prevent the automatic closure of the command box. |
Example batch file:
1@echo off
2echo Changing folders
3cd /d E:
4cd E:\VIIA\name_of_the_project_folder\name_of_the_analysis_folder
5
6echo Running the analysis
7diana -m "name_data_file" "name_dcf_file.dcf" name_fo_filosfile.ff
8
9echo Remove filos file
10del name_fo_filosfile.ff
11
12pause
What to check during a calculation?
Non-linear finite element calculation will take a considerable amount of time. To prevent wasting time, it’s good to have some intermediate checks during the calculation. Four basic check’s should be performed.
Disk size and filos-file size
To be checked during the analysis. If filos-file is bigger then 40Gb you are probably asking too many result items.
Setup of the model
During the setup of the model no warnings or errors should occur. This can be check in the out-file. Note that this
should be done after each setup. For a phased analysis the model is setup each phase.
Convergence behaviour
The convergence behaviour gives a good impression of smoothness of the calculation process. When many steps does not
convergence the calculations commands might need to be adjusted. Already, during the calculation
_viia_congergence_graph() can be used to create a graph. Also, the out-file can bechecked manually by searching for ‘NO CONVERGENCE’.
Displacement field
It is possible that the during the calculation a mathematical possible solution is found which is not a physical valid
one. To discover this kind of problems the displacement field should be checked. Especially calculations with
arc-length control should be checked with care.
Maximum crackwidth
If applicable crackwidth give a good indication of the validity of the results. Very large cracks are probably
unrealistic. Note that for large models a large local crack does not necessarily result in bad convergence. The
convergence behaviour is related to the out-of-balance of the entire model. For large models local non-linear
behaviour does not result in bad convergence.
Residual forces
When the FEM-solver tries to calculate proper internal forces. The mismatch of the internal forces is stored as residual
forces. These shouldn’t be to high.
When to stop a calculation?
The setup of the model should be done correctly. If problems occur in this process one should stop the calculation and refine the model of calculation commands.
The convergence behaviour, displacement field, maximum crackwidth and residual forces combined should be used to check the validity of the calculation. If one of those gives an indication something is wrong which cannot be explained by the other ones, the calculation can better be stopped.
How to create, analyse and handle results in one flow
You can perform the whole workflow on the server, which is especially useful if you are doing your final 7 signal calculation for NLTH. Instructions and template script can be found in the howto guide: How to use template script for server.
What to do if your calculation is finished?
After the calculation is finished several steps has to be taken to free up space for other calculations:
Remove the filos-file (also out of recycle bin) if this is not already done by the batch file.
Check if the results are useful/valid otherwise remove all the files, then you are done.
If applicable, preform the result handling on the server.
Copy all the necessary files to your local system. (if necessary one can request a portable hard disk drive).
If applicable, preform the result handling on your local system.
Make sure the data-, dcf- and out-file are stored in a place with proper back-up facilities, like BOX.
Remove all the result files from the server.
What to do if your project is finished?
After a project is finished all the data should be removed from the server. The data-, dcf- and out-file can be stored somewhere else if not already done.
Reset password for SZ1 account
The password for the SZ1 account might expire. If that is the case you will not be able to login to the server. The following procedure can be used to reset your password:
Login to any of the below mentioned links. (Log out from the current session if you are already logged in):
Enter username as SZ1-XXXXXX-ADM@corporateroot.net and Click on Next.
Then enter your current password and click on Sign in.
Now, please reset your new password based on the below new password policy. Minimum password length is 15 characters. It cannot be the same as any of the previous 5 passwords, requires any 3 combinations out of 4 mentioned below:
English uppercase characters (A through Z).
English lowercase characters (a through z).
Base-10 digits (0 through 9).
Non-alphanumeric (for example, $, #, %). extended ASCII, symbolic, or linguistic characters.
Note
Password cannot contain any personal information.
Do not use a sequenced approach to passwords: Password01 becomes Password02 and with the next change it becomes Password03.